CartoDB Intro Workshop for Madlan
- Trainer: Ramiro Aznar · ramiroaznar@cartodb.com · @ramiroaznar
- June 23th 2016
- CartoDB Introductory Workshop for Madlan
http://bit.ly/madlan
Map Academy, tutorials and other online resources
Further questions and troubleshooting
- Email to support@cartodb.com.
- Some questions could be already anwered at GIS Stack Exchange
cartodbtag.
Contents
1. Importing datasets
1.1 Supported Geospatial Data Files
CartoDB supports the following geospatial data formats to upload vector data*:
ShapefileKMLKMZGeoJSON*CSVSpreadsheetsGPXOSM
Importing different geometry types in the same layer or in a FeatureCollection element (GeoJSON) is not supported. More detailed information here.
[*] More detailed information about GeoJSON format here, here and here.
1.2 Common importing errors
- Dataset too large:
- File size limit: 150 Mb (free).
- Import row limit: 500,000 rows (free).
- Solution: split your dataset into smaller ones, import them into CartoDB and merge them.
- Malformed CSV:
- Solution: check termination lines, header…
- Encoding:
- Solution:
Save with Encoding>UTF-8 with BOMin Sublime Text, any other decent text editor or iconv.
- Solution:
- Shapefile missing files:
- Missing any of the following files within the compressed file will produce an importing error:
.shp: contains the geometry. REQUIRED..shx: contains the shape index. REQUIRED..prj: contains the projection. REQUIRED..dbf: contains the attributes. REQUIRED.
- Other auxiliary files such as
.sbn,.sbxor.shp.xmlare not REQUIRED. - Solution: make sure to add all required files.
- Missing any of the following files within the compressed file will produce an importing error:
- Duplicated id fields:
- Solution: check your dataset, remove or rename fields containing the
idkeyword.
- Solution: check your dataset, remove or rename fields containing the
- Format not supported:
- URLs -that are not points to a file- are not supported by CartoDB.
- Solution: check for missing url parameters or download the file into your local machine, import it into CartoDB.
- Non supported SRID:
- Solution: try to reproject your resources locally to a well known projection like
EPSG:4326,EPSG:3857,EPSG:25830and so on.
- Solution: try to reproject your resources locally to a well known projection like
Other importing errors and their codes can be found here.
2. Getting your data ready
2.1 Geocoding
If you have a column with longitude coordinates and another with latitude coordinates, CartoDB will automatically detect and covert values into the_geom. If this is not the case, CartoDB can help you by turning the named places into best guess of latitude-longitude coordinates:
- By Lon/Lat Columns.
- By City Names.
- By Admin. Regions.
- By Postal Codes.
- By IP Addresses.
- By Street Addresses.
Know more about geocoding in CartoDB here.
2.2 Datasets
These are the datasets we are going to use on our workshop. You’ll find them all on our Data Library:
- Populated Places [
ne_10m_populated_places_simple]: City and town points. - World Borders [
world_borders]: World countries borders.
2.3 Simple SQL operations
Selecting all columns:
SELECT
*
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple;
Selecting some columns:
SELECT
cartodb_id,
name as city,
adm1name as region,
adm0name as country,
pop_max,
pop_min
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
Selecting distinct values:
SELECT DISTINCT
adm0name as country
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
2.4 Filtering
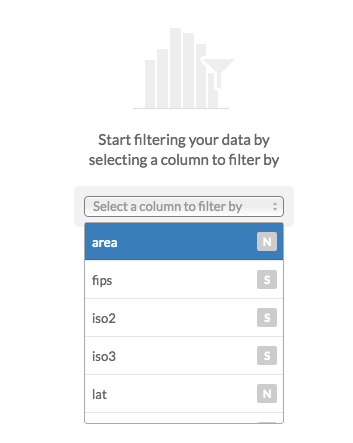
Filtering numeric fields:
SELECT
*
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
WHERE
pop_max > 5000000;
Filtering character fields:
SELECT
*
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
WHERE
adm0name ilike 'spain'
Filtering a range:
SELECT
*
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
WHERE
name in ('Madrid', 'Barcelona')
AND
adm0name ilike 'spain'
Combining character and numeric filters:
SELECT
*
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
WHERE
name in ('Madrid', 'Barcelona')
AND
adm0name ilike 'spain'
AND
pop_max > 5000000
2.5 Others:
Selecting aggregated values:
count
SELECT
count(*) as total_rows
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
sum
SELECT
sum(pop_max) as total_pop_spain
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
WHERE
adm0name ilike 'spain'
avg
SELECT
avg(pop_max) as avg_pop_spain
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
WHERE
adm0name ilike 'spain'
Ordering results:
SELECT
cartodb_id,
name as city,
adm1name as region,
adm0name as country,
pop_max
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
WHERE
adm0name ilike 'spain'
ORDER BY
pop_max DESC
Limiting results:
SELECT
cartodb_id,
name as city,
adm1name as region,
adm0name as country,
pop_max
FROM
ne_10m_populated_places_simple
WHERE
adm0name ilike 'spain'
ORDER BY
pop_max DESC
LIMIT 10
3. Making our first map
3.1 Wizard
Analyzing your dataset… In some cases, when you connect a dataset and click on the MAP VIEW for the first time, the Analyzing dataset dialog appears. This analytical tool analyzes the data in each column, predicts how to visualize this data, and offers you snapshots of the visualized maps. You can select one of the possible map styles, or ignore the analyzing dataset suggestions.
- Simple Map
- Cluster Map
- Category Map
- Bubble Map
- Torque Map
- Heatmap Map
- Torque Cat Map
- Intensity Map
- Density Map
- Choropleth Map:
Know more about chosing the right map to make here.
3.2 Styles
The last link in the website referenced above is a great discussion about the different maps CartoDB allows to create.
Simple Map:
/** simple visualization */
#layer{
polygon-fill: #FF6600;
polygon-opacity: 0.7;
line-color: #FFF;
line-width: 0.5;
line-opacity: 1;
}
Choropleth Map:
Before making a choropleth map, we need to normalize our target column. For that, we need to divide the population by the area.
SELECT
wb.*,
pop2005/(ST_Area(the_geom::geography)/1000000) AS pop_norm
FROM
world_borders wb
Click on ‘create new dataset from query’.
Rename the new dataset to world_borders_norm
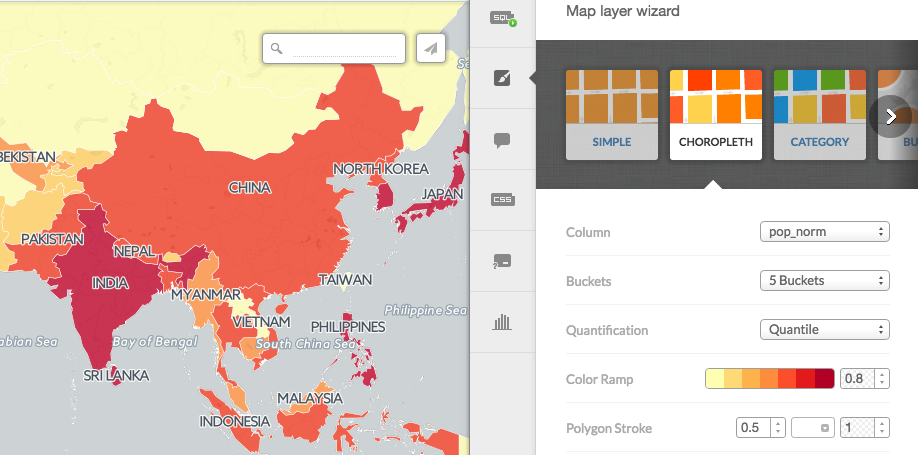
/** choropleth visualization */
#layer{
polygon-fill: #FFFFB2;
polygon-opacity: 0.8;
line-color: #FFF;
line-width: 0.5;
line-opacity: 1;
}
#layer [ pop_norm <= 247992435.530086] {
polygon-fill: #B10026;
}
#layer [ pop_norm <= 4086677.23673585] {
polygon-fill: #E31A1C;
}
#layer [ pop_norm <= 1538732.3943662] {
polygon-fill: #FC4E2A;
}
#layer [ pop_norm <= 923491.374542489] {
polygon-fill: #FD8D3C;
}
#layer [ pop_norm <= 616975.331234902] {
polygon-fill: #FEB24C;
}
#layer [ pop_norm <= 326396.192958792] {
polygon-fill: #FED976;
}
#layer [ pop_norm <= 95044.5589361554] {
polygon-fill: #FFFFB2;
}
Proportional symbols map
Take a look on this excellent blog post by Mamata Akella regarding how to produce proportional symbols maps. The easiest ones being buble maps since it’s directly supported by CartoDB wizards. The other type, the graduated symbols where you compute the radius of the symbol to be used later on the CartoCSS* section needs a bit of SQL computation but nothing hard.
WITH aux AS(
SELECT
max(pop2005) AS max_pop
FROM
world_borders
)
SELECT
cartodb_id,
pop2005,
ST_Centroid(the_geom_webmercator) AS the_geom_webmercator,
5+30*sqrt(pop2005)/sqrt(aux.max_pop) AS size
FROM
world_borders,
aux
#layer{
marker-fill-opacity: 0.8;
marker-line-color: #FFF;
marker-line-width: 1;
marker-line-opacity: 1;
marker-width: [size];
marker-fill: #FF9900;
marker-allow-overlap: true;
}
[*] Know more about CartoCSS with our documentation and try our cartoColors!
3.3 Other elements
Basemaps:
Options:
Legend:
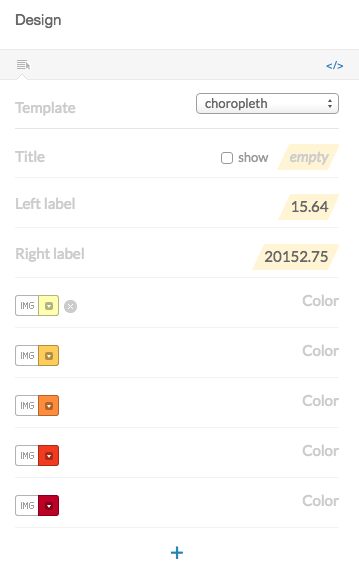
By clicking on the </> icon, you would see and edit the source HTML code.
<div class='cartodb-legend choropleth'>
<div class="legend-title">Total Population</div>
<ul>
<li class="min">
95044.56
</li>
<li class="max">
247992435.53
</li>
<li class="graph count_441">
<div class="colors">
<div class="quartile" style="background-color:#FFFFB2"></div>
<div class="quartile" style="background-color:#FED976"></div>
<div class="quartile" style="background-color:#FEB24C"></div>
<div class="quartile" style="background-color:#FD8D3C"></div>
<div class="quartile" style="background-color:#FC4E2A"></div>
<div class="quartile" style="background-color:#E31A1C"></div>
<div class="quartile" style="background-color:#B10026"></div>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
Labels:
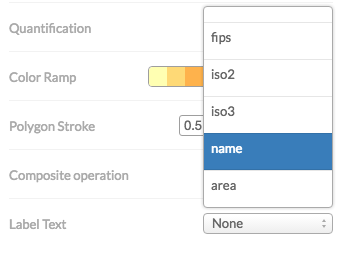
Selecting a field in the wizard will produce the following CartoCSS code to render the labels.
#world_borders::labels {
text-name: [name];
text-face-name: 'DejaVu Sans Book';
text-size: 10;
text-label-position-tolerance: 10;
text-fill: #000;
text-halo-fill: #FFF;
text-halo-radius: 1;
text-dy: -10;
text-allow-overlap: true;
text-placement: point;
text-placement-type: simple;
}
This also shows an important concept for CartoCSS. you can specify more than one rendering pass for your features. This means that using the #layername::passname notation you can render more than one symbol on your features.
Infowindows and tooltip:
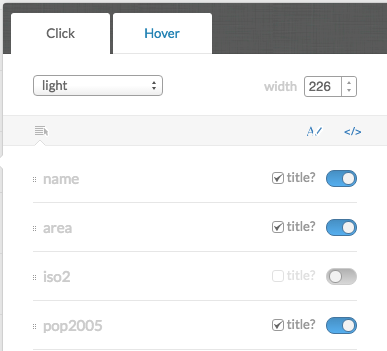
Clicking on the </> will also show the source code for the Infowindows.
<div class="cartodb-popup v2">
<a href="#close" class="cartodb-popup-close-button close">x</a>
<div class="cartodb-popup-content-wrapper">
<div class="cartodb-popup-content">
<h4>country</h4>
<p>{{name}}</p>
<h4>population</h4>
<p>{{pop_norm}}</p>
<h4>area</h4>
<p>{{new_area}}</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="cartodb-popup-tip-container"></div>
</div>
Title, text and images:
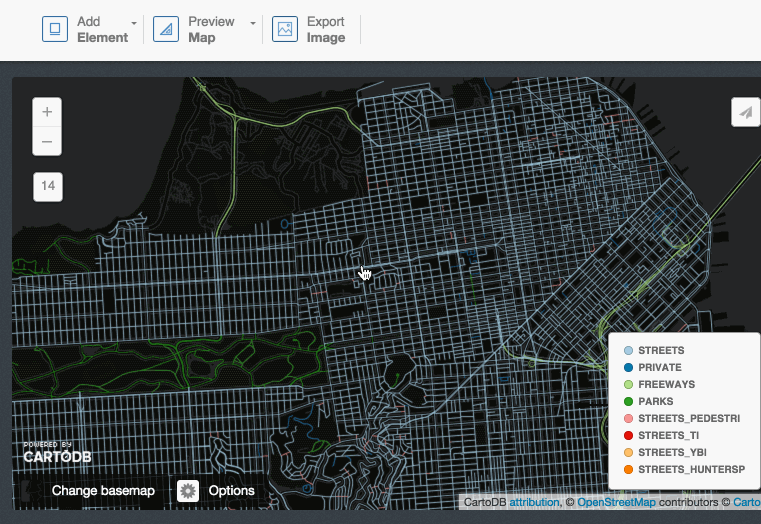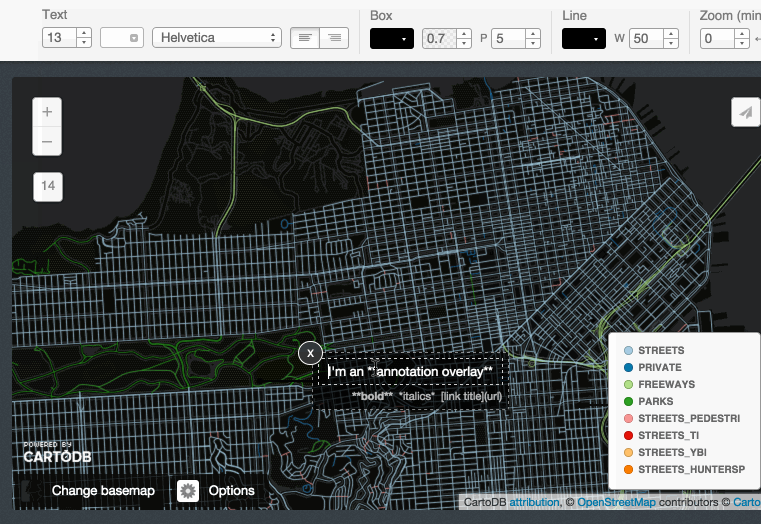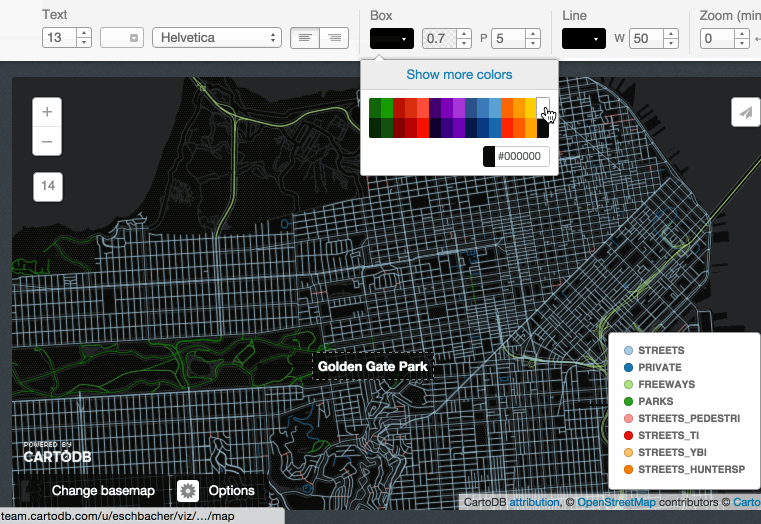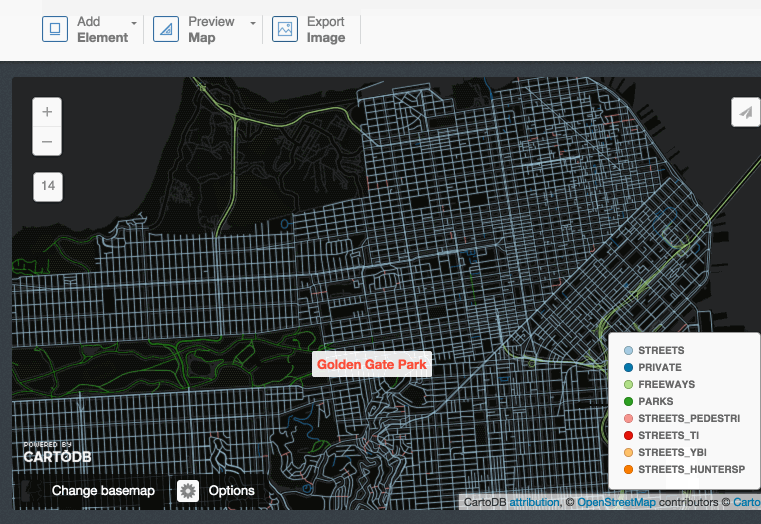
3.4 Share your map!
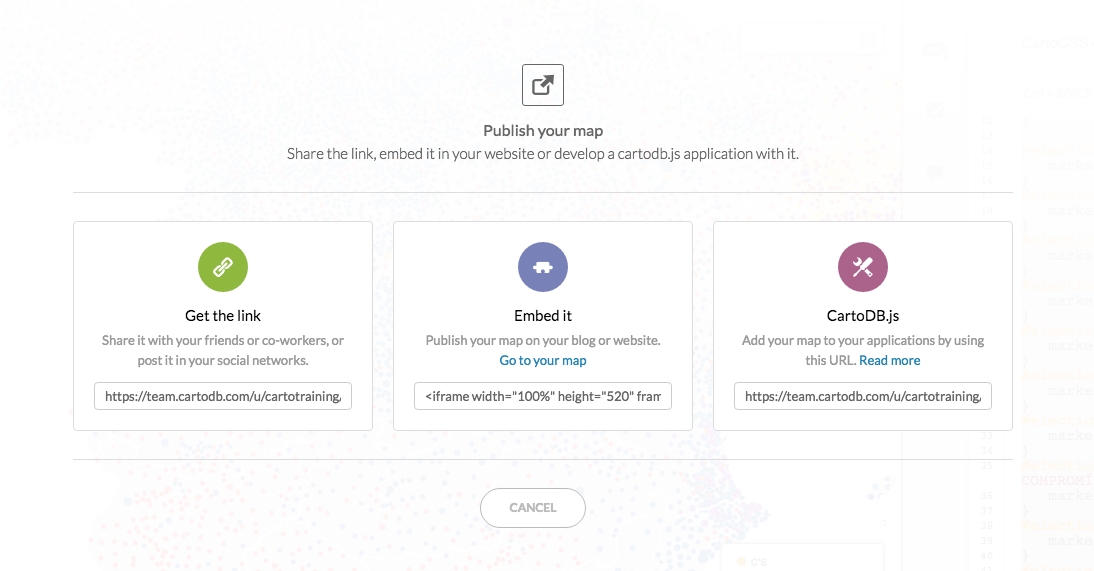
Get the link:
https://team.cartodb.com/u/cartotraining/viz/36d25ff0-2189-11e6-b39e-0e787de82d45/public_map
Embed it:
<iframe width="100%" height="520" frameborder="0" src="https://team.cartodb.com/u/cartotraining/viz/36d25ff0-2189-11e6-b39e-0e787de82d45/embed_map" allowfullscreen webkitallowfullscreen mozallowfullscreen oallowfullscreen msallowfullscreen></iframe>